- Infection Diseases - Welcome
- Infectious Disease
- Clinical Case
- Tips for Patients
- CIMS Infectious Disease Unit
- Videos
Welcome to the Infection Diseases Section of the website.
Infectious diseases (ID) refer to the diseases spread by infectious agents like bacteria, viruses, fungi and parasites. They are also known as communicable diseases, as they are transmitted from the reservoir/source of infection to the susceptible host.
Dynamics of Diseases Transmission Disease spread requires a susceptible host and an infective agent, in an environment that brings them together:
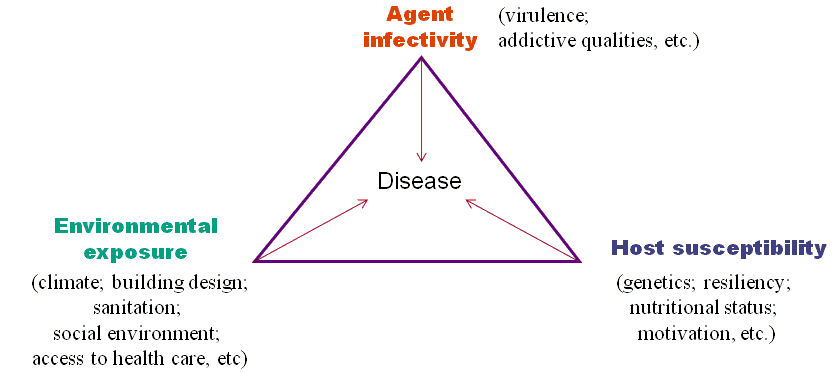
Mode of Transmission of Infection
Infectious diseases can be transmitted in many different ways.
Indirect Transmission
Vehicle Borne Infections: Transmission through vehicles like water, food, etc. could produce infectious diseases like typhoid and acute diarrhea

Vector Borne Infections: Vectors like mosquito, flies, ticks, etc. serves as a living carrier that transport an infectious agent to the host like Malaria, Dengue, Chikungunya, Tick fever .

Air borne Infections: They are spread through very small saliva/cough droplets in the air. Examples include , Tuberculosis, Measles, Chickenpox, Swine flu.
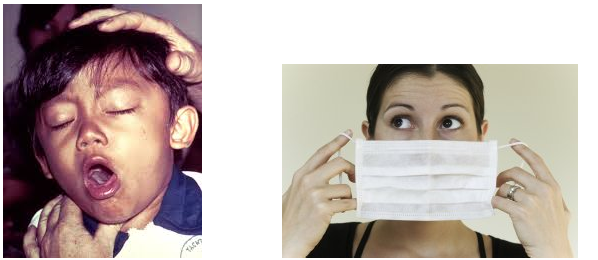
 |
Fomite Borne Infections:Fomites are non-living objects other than water or food e.g. soiled clothes, towels, which could transmit infections like diarrhea, eye and skin infections etc. |
| Unclean hands and fingers: It could lead to intestinal infections |  |
Direct Transmission:
 |
Direct Contact:Unsafe (without condom) physical contact may lead to serious infectious diseases like HIV infection and AIDS, and other sexually transmitted diseases. |
| Contact with soil: Contact of soil possessing infective agent may lead to various parasitic infections like hookworm infections and serious diseases like tetanus. |  |
 |
Direct Skin Inoculation: Infective agents may enter into the body through animal bite e.g. rabies due to dog bite; contaminated needles could cause hepatitis B and HIV infection |
| Apart from these routes, infected preganant mother could also transmit infection to the child (through placenta) e.g. rubella, HIV, etc. |  |
How to prevent infectious diseases?
Immunization
Vaccination for prevention of infectious diseases is of utmost importance in this era of globalization, increasing life expectancy, growing population of immune-compromised patients and migration and increasing international travel.
Timely and comprehensive immunization ensures safety against a number of life threatening infections and saves a lot of money and manpower which gets involved in their treatment.
Marengo CIMS Hospital Vaccination Centre offers basic immunization to all. Specific adult vaccines which are also offered are as follows:
- Pneumococcal vaccination for elderly people; chronic heart, lung, liver disease patients; HIV patients, diabetic patients, etc.
- Influenza vaccination for patients with chronic diseases.
- Chickenpox vaccination for patients without immunity to the virus.
- Human Papilloma Virus vaccination for young females.
- Typhoid vaccination
- Advice to national and international travelers regarding specific vaccinations and other measures to protect them from infections endemic in those regions
Travel Medicine
Travel medicine is devoted to the health of travelers who visit foreign countries. It is an interdisciplinary specialty concerned not only with prevention of infectious diseases during travel, but also with the personal safety of travelers and the avoidance of environmental risks.
Travel medicine standards are increasingly based on evidence and are moving away from reliance on the opinion of experts.
The various measures include pre-travel risk assessment, pre-travel advice, immunization of the travelers and post-travel care.
Infection Control and Antibiotic Stewardship
Infection control is a clinical practice especially oriented to reduce incidence of healthcare/hospital associated infections (HAI). The types of HAI includes Ventilator Associated Pneumonia (VAP), CLABSI (Central line associated Blood Stream Infection), Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) and Surgical Site Infection (SSI). As per quality measure guidelines, Healthcare Organization’s performance quality could be realized by comparing hospitals pooled data with Standard Benchmarks.
Antibiotic Stewardship: It is a multi-disciplinary approach for rational use of appropriate antibiotics so as to produce effective clinical impact. It includes entire health care system stakeholders.It recommends pro-active surveillance, patient counseling with help of clinical pharmacists and also drug utilization studies especially where guidelines are not available.
Good Hand Hygiene Practices
Washing hands is not just a procedure, but also a scientific step-wise technique. It is globally recommended to follow the method given below for hand washing to avoid chances of infections maximally.


Infectious Diseases: An Indispensable Specialty:
- Antibiotic Resistance:: Frequent doses of same antibiotics over a long period of time renders patient with “no effect” condition even after higher doses. This condition is called “antibiotic resistance”. Treating resistant microbes has become an evidence-based-art.
- Recurrence/Relapse: : Due to ineffectiveness of antibiotics due to resistance or other reasons, susceptibility of host to disease causing organism increases. This results in re-development of disease symptoms.
- Misuse of Antibiotics: It has become a tendency to administer antibiotics even for self –limiting infections, which otherwise could be treated symptomatically. Irrational drug prescription leads to misuse of antibiotics contributing further to drug resistance.
- No newer antibiotic in pipeline
- Need of the hour: The expertise of ID (Infectious Disease) specialist becomes important for the appropriate management of infections like multi-drug resistant (MDR tuberculosis, myriad of infections in HIV patients, emerging tropical and viral infections; infections in the immune-compromised like nocardia, mucor, aspergillus,cryptococcus, cytomegalovirus, pneumocystis, etc.)
Clinical Case at CIMS Infectious Disease Unit
- If you are having low grade fever, weight loss, decreased appetite and localizing symptoms like cough, abdominal pain, headache, etc. going on for a long time, you could be suffering from tuberculosis. Please don’t neglect and contact your doctor immediately.
- TB (tuberculosis) which is not responding to the treatment may be drug resistant and may need change in the treatment without delay.
- Symptoms like cough, sore throat, running nose, redness of eyes, body ache, fever are suggestive of flu; but if they are complicated by difficulty in breathing, loose motions, decreased urine output, abnormal behavior, etc. it may not be common flu, and may need treatment with antiviral drugs.
- Dengue, malaria, chikungunya are some of the common infections spread by mosquitoes. Protect yourself from mosquitoes by using mosquito repellants and nets.
- Dengue fever, most of the times, is self-limiting; but appearance of abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, bleeding, jaundice, decreased urine output are some of the alarming symptoms.
- HIV is no more a ‘Non-treatable’ disease. Early initiation of treatment is associated with very good outcomes and a normal healthy living.
With help of a full-time dedicated Infectious Diseases consultant, we are committed to provide in-patient and out-patient care for:
- HIV and AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome)
- Pulmonary and extra pulmonary tuberculosis, including MDR (Multi-drug resistant) and XDR (Extensively drug-resistant) TB
- Community acquired infections like upper respiratory infections, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, brain infections, etc.
- Tropical infections like malaria, dengue, typhoid fever, chikungunya
- Opportunistic fungal infections like candidiasis, aspergillosis, and mucormycosis in immuno-compromized patients
- Hospital acquired infections, post-surgical infections
- Infections in cancer patients
- Infections in organ transplant recipients
Additionally, we also practice antimicrobial stewardship programme at CIMS
English Videos
[yotuwp type=”videos” id=”S5pS3cXPbJg” ]
Gujarati Videos
[yotuwp type=”videos” id=”wqTbxL92nu4″ ]
Hindi Videos
[yotuwp type=”videos” id=”QwLqd7HMVCg” ]

Contact Us
Toll Free Number : 1800 309 9999
Medical Helpline +91 70 69 00 00 00
Phone: 079 4805 1200 or 1008
+91 79 2771 2771 or 72
Fax: +91 79 2771 2770
Mobile: +91 98250 66664 or +91 98250 66668
Ambulance: +91 98244 50000
Email: info@cims.org | opd.rec@marengoasia.com
Location
CIN No: U85110GJ2001PTC039962
