Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis refers to the buildup of fats, cholesterol and other substances in and on artery walls (plaque), which can restrict blood flow. The plaque can burst, triggering a blood clot. Although atherosclerosis is often considered a heart problem, it can affect arteries anywhere in body. It may be preventable and is treatable
It is the usual cause of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral vascular disease. Most adults older than 60 have some atherosclerosis, but most don’t have noticeable symptoms.
What are the Causes of Atherosclerosis?
- High blood pressure
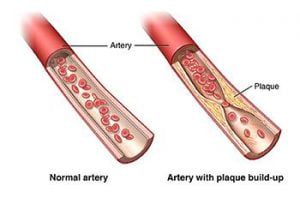
- High cholesterol
- High triglycerides, a type of fat (lipid) in blood
- Smoking and other sources of tobacco
- Insulin resistance, obesity or diabetes
- Inflammation from diseases, such as arthritis, lupus or infections, or inflammation of unknown cause
What are the Symptoms?
Atherosclerosis develops gradually. Mild atherosclerosis usually doesn’t have any symptoms. Symptoms of moderate to severe atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are affected. For example:
- Atherosclerosis in heart arteries results into chest pain or pressure (Angina)
- Atherosclerosis in arteries leading to brain results into numbness or weakness in arms or legs, difficulty in speaking, temporary loss of vision, this may also progress to stroke if left untreated.
- Atherosclerosis in arteries of legs and arms causes pain in leg while walking (claudication).
- Atherosclerosis in arteries leading to kidney results into kidney failure or high blood pressure.
How to Diagnose?
- Chest X-ray
- ECG (Electrocardiogram)
- Holter and Event Monitors
- Echocardiography
- Stress Test
- Computed Tomography Scan or CT Angiogram
- Coronary Angiography
What are the Treatment Modalities?
Medication: Various medications are used for treatment of atherosclerosis. They could also reduce the risk of hearts attack and strokes.
- Drugs like Statins to Lower Bad Cholesterol i.e.LDL. like atorvastatin, fluvastatin , lovastatin, pravastatin, pitavastatin, simvastatin, rosuvastatin
- Drugs like Fibrates to Reduce Triglycerides like clofibrate ,gemfibrozil ,fenofibrate
- Niacin to Improve Overall Cholesterol
- Antihypertensive Drugs to control High Blood Pressure
- Antiplatelet Drugs to Reduce the Risk of Blood Clots in the arteries
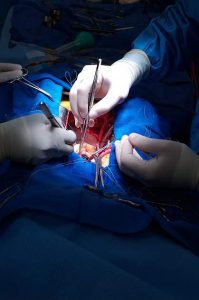
Invasive techniques to open blockages from atherosclerosis
- Angioplasty: A thin tube is inserted into an artery from a leg or arm which travels to diseased arteries. A blocked artery is opened by stent through the same tube.
- Coronary artery bypasses grafting (CABG) surgery: An open heart surgery in which a healthy blood vessel, often from leg or chest is used to bypass a blocked artery.
How to Prevent Atherosclerosis?
- Avoid fatty foods and eat well-balanced meals that are low in fat and cholesterol.
- Include several daily servings of fruits and vegetables and add fish to diet at least twice a week may be helpful.
- Limit alcohol to probably one drink a day for women, two a day for men.
- Exercise for 30 minutes a day if not overweight, and for 60 – 90 minutes a day if overweight.
- Quit smoking.
- Get blood pressure checked every 1 – 2 years before age 50 and yearly after age 50.
What are the Complications?
The complications of atherosclerosis depend on which arteries are blocked. For example:
- Coronary artery disease. When atherosclerosis narrows the arteries close to heart, one can develop coronary artery disease, which can cause chest pain (angina), a heart attack or heart failure.
- Carotid artery disease which can cause a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or stroke.
- Peripheral artery disease may develop circulation problems in arms and legs. In rare cases, poor circulation can cause tissue death (gangrene).
- Aneurysm is a bulge in the wall of artery. Pain and throbbing in the area of an aneurysm may occur and it is a medical emergency.

