ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
ADHD stands for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, a condition with symptoms such as inattention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity. Symptoms differ from person to person. ADHD was previously called ADD, or attention deficit disorder. Both children and adults can have ADHD, but symptoms always start in childhood. Adults with ADHD may have trouble managing time, getting organized, setting goals, and keeping a job.

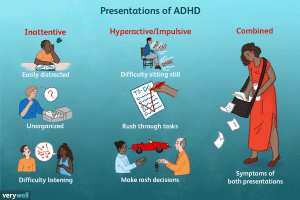
What are the Symptoms of ADHD?
There are three groups of symptoms:
- Inattention
- Hyperactivity
- Impulsivity
Inattention
It may not be noticed until a child goes to school. In adults, it may be easier to notice it at work or in social situations.
The person may procrastinate, fail to complete tasks such as chores or household chores, or often move from one incomplete activity to another.
They could also be :
- Disorganized
- Have lack of focus
- Have difficulty paying attention to detail and a tendency to make careless mistakes. The performed work can be messy and seem sloppy.
- Has trouble staying on topic while speaking, doesn’t listen to others, and doesn’t follow social rules
- Forgets about daily activities (eg, missing appointments, forgetting to bring lunch)
- Gets easily distracted by things like trivial noises or events that others generally ignore.
Hyperactivity
It can vary with age. It can be noticed it preschoolers. ADHD symptoms almost always appear before high school.
Children with hyperactivity can:
- Shake and squirm when sitting.
- Get up frequently to walk or run.
- Running or climbing a lot when not appropriate. (In adolescents, this may seem uneasy.)
- Have trouble playing quietly or doing hobbies quietly.
- Always be “on the way”
- Talk excessively
Toddlers and preschoolers with ADHD tend to be constantly on the go, jumping on furniture and having trouble participating in group activities that require them to sit still. For example, they may have difficulty hearing a story.
Hyperactivity can appear as feelings of restlessness in adolescents and adults. They may also have difficulty doing quiet activities where you sit still.
Impulsiveness
Symptoms of this include:
- Impatience
- Having difficulty waiting to speak or react
Impulsiveness can cause accidents, such as knocking down objects or hitting people. Children with ADHD can also do risky things without stopping to think about the consequences. For example, they can climb and put themselves in danger.
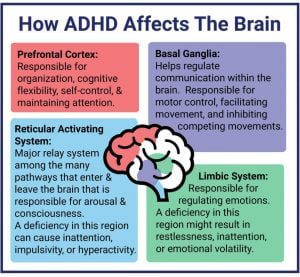
Different Brain Areas Affected by ADHD
How to Diagnose ADHD?
There is no single test to diagnose ADHD. Experts diagnose ADHD after a person has shown some or all of the symptoms on a regular basis for more than six months and in more than one setting.
Diagnosis of ADHD in Children

There are standard guidelines for diagnosis of ADHD. Health care providers, such as pediatricians, psychiatrists, and child psychologists, can diagnose ADHD with the help of these guidelines. Diagnosis involves gathering information from various sources, including schools, caregivers, and parents.
The health care provider verifies the behaviour that is:
- It is not typical for the person’s age. (However, most children may behave that way at one time or another.)
- It has a negative impact on the person’s ability to function at home, in social settings or at work.
To diagnose ADHD,
– Complete detail medical history
– Complete physical exam, which includes vision and hearing exams
– Neuropsychiatric EEG-Based Assessment Assist System
Theta / beta ratio has been shown to be higher in children and adolescents with ADHD than in children without it. The scan is approved for use in people ages 6 to 17, should be used as part of a comprehensive medical and psychological exam.
– Psychological tests.
Certain conditions that could mimic ADHD or cause ADHD-like behaviours are:
- Important recent life changes (such as divorce, death in the family, or recent move)
- Undetected seizures
- Thyroid problems
- Sleeping problems
- Anxiety
- Depression
- lead toxicity
Diagnosis of ADHD in Adults
It is not easy for a healthcare provider to diagnose ADHD in an adult. Sometimes an adult will recognize ADHD symptoms on its own when a son or daughter is diagnosed. Other times, they will seek professional help for themselves and discover that their depression, anxiety, or other symptoms are related to ADHD.
What are Treatment Options?
Treatment plans may include drug treatment (medications) and non-drug treatment that includes special education programs and psychological intervention.
Studies show that long-term treatment with a combination of drugs and behavioral therapy is much better than just drug treatment. Children treated with ADHD medication and therapy also had better social skills.
Medicines
Medication is an important part of your ADHD treatment. Doctors can choose from many types of medications to control the symptoms of the disorder.
The most commonly used to treat ADHD include:
Stimulants– This group of medications has treated ADHD for several decades. These medications can help you focus your thoughts and ignore distractions. Stimulant medications work for 70% to 80% of people. They are used to treat moderate and severe ADHD. They can be helpful for children, teens, and adults who have difficulties at school, work, or home.
Antidepressants – People with ADHD often also have depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. They can take an antidepressant to control mental health problems or other conditions along with a stimulant for ADHD.
Non-pharmacological Therapies
If your child has been diagnosed with ADHD, you want to know what can help him. Medication is not the only way to treat it. Other things can also help. And many can be used in conjunction with medications or other non-drug treatments. Talk to your doctor to come up with a treatment plan that works best for your child.
Behavioural therapy

This type of therapy, also known as cognitive behavioural therapy, can ease your child’s ADHD symptoms and help them feel better. Most of the time, it focuses on identifying and changing thoughts to change behaviour. Research shows that it is very good at improving mindfulness and reducing impulsive behaviour. People with ADHD often have mental health problems like depression or anxiety, and behavioural therapy also helps with these too. Behavioural therapy works best in combination with drugs.
Coaching
This is a newer type of treatment for ADHD. They use different techniques during coaching. They help children and adults with ADHD learn skills that help them manage symptoms. For example, coaches can help with goal setting, problem solving, and time management.
Neuro-Feedback
Neurofeedback, also called brain training or biofeedback EEG; improves some children’s ability to pay attention, manage time, and stay on task. It is also shown to reduce impulsive and anxious behaviour.
Music Therapy
Children with ADHD often struggle with stress and anxiety. Music can be relaxing, which is why some experts think it is a good medicine. Most ADHD professionals use it in conjunction with other treatments.
Assistive Technology (AT)
Some parents find that assistive technology, such as cell phone apps, online calendars, screen readers, and talking calculators, help children pay attention.
Exercise
Regular exercise alleviates many symptoms of ADHD. It can help children pay attention and it can also improve their mood. Even small bursts of physical activity can raise levels of brain chemicals like dopamine. Activity also helps with sleep.
Healthy diet
Experts say that a nutritious diet full of fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is important for healthy brain development.
Supplements
With vitamins and minerals as a part of diet the brain stays healthy.Some research suggests that zinc supplements may help children with ADHD become less hyperactive and impulsive. Other studies show that fish oil supplements may also help with ADHD symptoms.

